반응형
Anaphylaxis
Introduction
- Serious allergic reaction
- Hypersensitivity는 일반적으로 무해한 antigens에 대한 부적절한 면역 반응
- Idiopathic anaphylaxis : 유발 원인이 확인되지 않은 경우

Pathophysiology
- IgE 매개로 mast cells, basophils activation
- Histamine, tryptase, carboxypeptidase A, proteoglycans 등 분비
- Prostaglandins, leukotrienes, platelet-activating factor 등 arachidonic acid metabolites 생성
- Inflammatory cytokine, tumor necrosis factor-α 등 분비
- 위의 매개 물질들의 overlapping, synergistic effec
Clinical features
- Pruritus, cutaneous, flushing, urticaria로 시작
- Fullness in the throat, anxiety, chest tightness, shortness of breath, lightheadedness 발생
- Complaint of a “lump in the throat”, hoarseness : Life-threatening laryngeal edema 전조 증상
- Abdominal pain, cramping, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, bronchospasm, rhinorrhea, conjunctivitis, hypotension 등 동반되기도 함. 악화되면 respiratory distress, decreased level of consciousness, circulatory collapse, cardiorespiratory arrest 발생
- 대부분 증상과 징후는 갑자기 발생. 대체로 항원 노출 후 60분 이내. 일반적으로 증상의 발현이 빠를수록 더 심한 반응. anaphylactic fatalities 50%가 한 시간 이내 발생
- 첫 증상과 징후가 사라지고 3~4시간 후, 초기 항원에 노출되고 8~11시간 후 second phase of mediator release에 의한 재발 가능성 있음. (biphasic phenomenon. 전향적 연구 결과 4~5% 정도 나옴)

Diagnosis
- 임상적으로 진단. 항원 노출된 이력이 명확하면 진단이 편함
- Hypotension, Airway compromise 유무에 관계 없이 두 가지 이상의 body systems involve 할 경우 anaphylaxis 의심
- Serum histamine levels, tryptase 등 혈액검사는 도움이 안 됨
Treatment
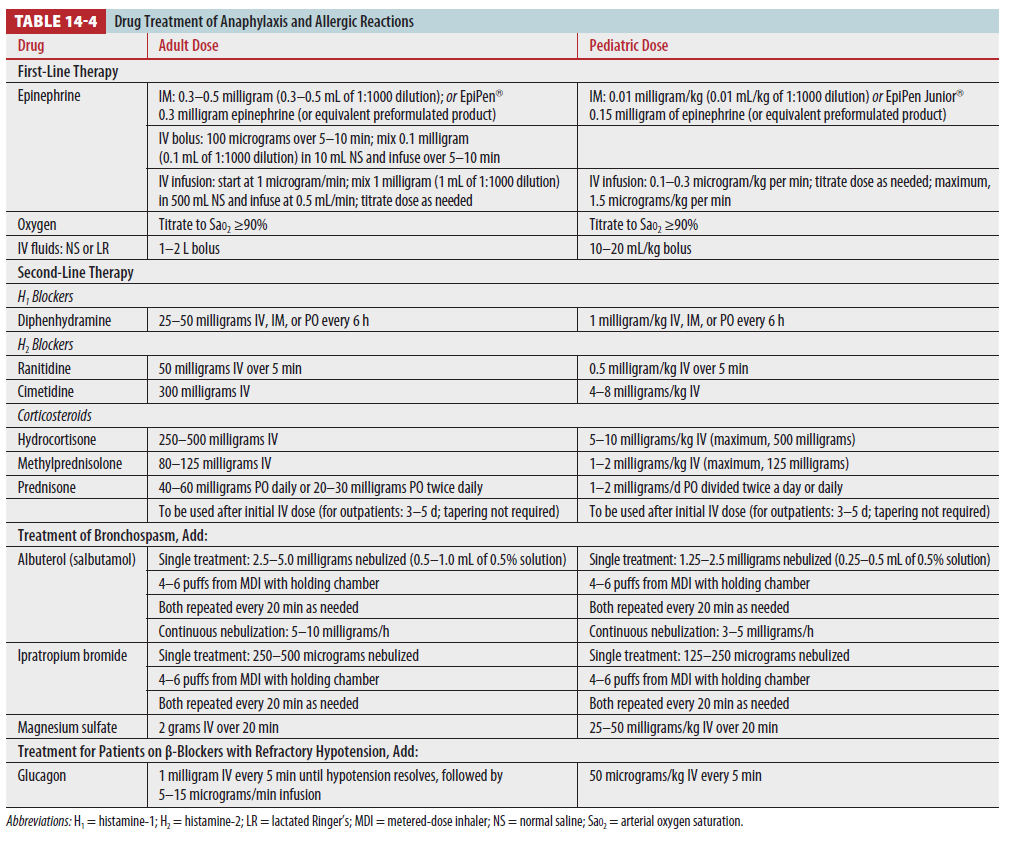
First-line therapies : Airway, Oxygen, Decontamination, Epinephrine, IV crystalloids
Airway & Oxygenation
- Uvula edema or hydrops, audible stridor, respiratory distress, hypoxia 확인
- Angioedema, respiratory distress → intubation!!
- O2 apply. PaO2 >90%
Decontamination
- Foodborne allergens : gastric lavage 비추천. 흡인 위험 높이고 적절한 처치 지연
- Insect stings : stinging remnants 제거
Epinephrine : Treatment of choice for anaphylaxis
- α1-receptor → Reduces mucosal edema, Treats hypotension
- β1-receptor → Increases HR, myocardial contractility
- β2-receptor → Bronchodilation, Limits further mediator release
- Cardiovascular compromise 징후 없으면 IM Thigh 0.3-0.5mg 투약
- 반복적 투약해도 호전이 없고 cardiovascular compromise 보이는 경우 IV bolus and/or infusion
- bolus isotonic crystalloid 1~2L (소아는 10~20 mL/kg)
Second-line treatments : Corticosteroids, Antihistamines, Inhaled bronchodilators, Vasopressors, Glucagon
* First-line treatments에 효과가 없거나 합병증 발생 또는 재발 방지를 위한 치료
Corticosteroids
- Protracted, biphasic reactions 막기 위해 사용
- Methylprednisolone, dexamethasone은 hydrocortisone, cortisone에 비해 mineralocorticoid effect가 비교적 적어 fluid retention이 문제되는 환자에서 선호
Antihistamines
- H1 antihistamine 필수적으로 사용 (diphenhydramine)
- circulatory shock 동반된 경우 H2 antihistamine 사용 (ranitidine, cimetidine 등)
- Shock 초기 치료에 반응이 없을 때
- IV EPi infusion으로 심각한 부정맥, 빈맥 발생할 때
- dopamine, dobutamine, epinephrine, norepinephrine, phenylephrine, vasopressin 사용
- Wheezing 있을 때 Inhaled albuterol/salbutamol
- 반응 없으면? inhaled anticholinergics, IV magnesium sulfate 추가
- IV aminophylline 비추. leukotriene receptor antagonists 효과적이지 않음
- β-blockers 사용하던 환자의 저혈압이 초기 치료에 반응 없을 경우
- 저혈압 해결될 때까지 glucagon 1mg IV 5분 간격으로 사용 후 infusion
Disposition and follow-up
- Severe allergic reactions, anaphylaxis 환자는 퇴원 시 Antihistamines, Corticosteroids (for 3~5 days), Epinephrine autoinjector 처방
- 모든 allergic reactions 환자는 퇴원 시 causative agent 회피할 수 있도록 하고, epinephrine autoinjector 사용법에 대해 교육해야 함

Allergies and Angioedema
Urticaria (hives)
- Pruritic, erythemic wheals 같은 of cutaneous reaction
Angioedema
- Urticaria 보다 깊음. dermis의 edema formation 특징적
- 주로 face, neck, distal extremities에 발생하고 airway obstruction 가능성 있음
- ACEi–induced angioedema
Food allergy reactions
- GI tract의 ingested food proteins → IgE-coated mast cells 자극 → hypersensitivity reactions
- Dairy products, eggs, nuts, and shellfish 등이 주요 원인
- Mammalian meat allergy/galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose (alpha-gal) allergy는 mammalian meat products에 대한 IgE-mediated allergic reaction. 최근 유병율 증가 추세
Allergic drug reactions
- 약물 부작용은 흔하며 이 중 true hypersensitivity reactions (IgE-mediated drug reactions) 10% 미만
- Penicillin은 allergic reactions 유발하는 가장 흔한 약물
- cephalosporins과의 cross-reactivity는 대략 10%. penicillin에 의한 심각한 부작용이 있었던 환자는 cephalosporins 역시 사용하지 말 것
- Allergic drug reactions 임상 증상은 매우 다양하며 circulating immune-complex에 의한 lupus-like reactions, serum sickness reactions 같은 generalized reaction 흔함
- Serum sickness
Reference
Tintinalli's Emergency Medicine, 9th, chapter 14, p.68~73
반응형
'의학자료 > Resuscitation' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 외상성 쇼크 Traumatic shock (0) | 2022.12.19 |
|---|---|
| 비외상성 쇼크 Nontraumatic shock (0) | 2022.12.18 |





